In the realm of sugary delights, maltose stands out as a harmonious union of two glucose molecules, joined by a pivotal bond called the glycosidic linkage. This intimate embrace bestows upon maltose its unique properties and myriad uses. In this enlightening narrative, we embark on a sugary adventure, exploring the intricacies of this glycosidic linkage, its formation, and the fascinating chemistry that underpins the sweetness of maltose.

Image: www.toppr.com
The glycosidic linkage, the covalent bond responsible for the marital bliss between the glucose subunits in maltose, is an intricate dance of hydroxyl groups and sugar molecules. Specifically, the alpha-1,4-glycosidic linkage in maltose manifests between the hydroxyl group on the first carbon of one glucose molecule and the fourth carbon of another. This molecular handshake creates a disaccharide with a linear structure, much like a molecular candy cane.
The formation of this glycosidic bond is meticulously orchestrated by the enzyme alpha-1,4-glucosidase, a biochemical maestro that facilitates the transfer of the glucose molecule from one sugar scaffold to another. This enzyme acts as a molecular matchmaker, bringing together the perfect pair and facilitating their bonding.
Once the glycosidic union is complete, maltose emerges with properties distinct from its glucose building blocks. Unlike glucose, which possesses a free aldehyde group, maltose lacks this reactive functional group. Instead, the aldehyde group of one glucose molecule becomes involved in the glycosidic linkage, leading to the stability and structural integrity of maltose.
This unique structure of maltose plays a significant role in its physiological and culinary significance. In our digestive system, enzymes such as maltase specifically cleave the glycosidic bond, releasing the individual glucose molecules for absorption and subsequent use as energy.
Maltose finds widespread application in the culinary realm as well. It contributes to the subtle sweetness of malt beverages, showcasing its natural sugary charm. Moreover, it serves as the primary ingredient in maltose syrup, a common ingredient in candy and other confections, imparting a delightful sweetness that dances upon the tongue.
Maltose also plays a crucial role in certain industries, particularly in the production of fermented beverages and baked goods. In brewing, maltose serves as the primary substrate for yeast metabolism, a process that leads to the production of ethanol and carbon dioxide, ultimately resulting in the delightful effervescence of our favorite beers and spirits. Similarly, in bread-making, maltose enhances the browning of the crust, contributing to that irresistible golden-hued perfection.
Our journey into the glycosidic linkage of maltose reveals a captivating tale of molecular harmony. This essential bond creates a disaccharide with unique properties and plays a pivotal role in various biological and culinary realms. From the sweet symphony of maltose syrup to the bubbling bliss of fermented beverages, the glycosidic linkage underpins the sugary wonders that enhance our lives.
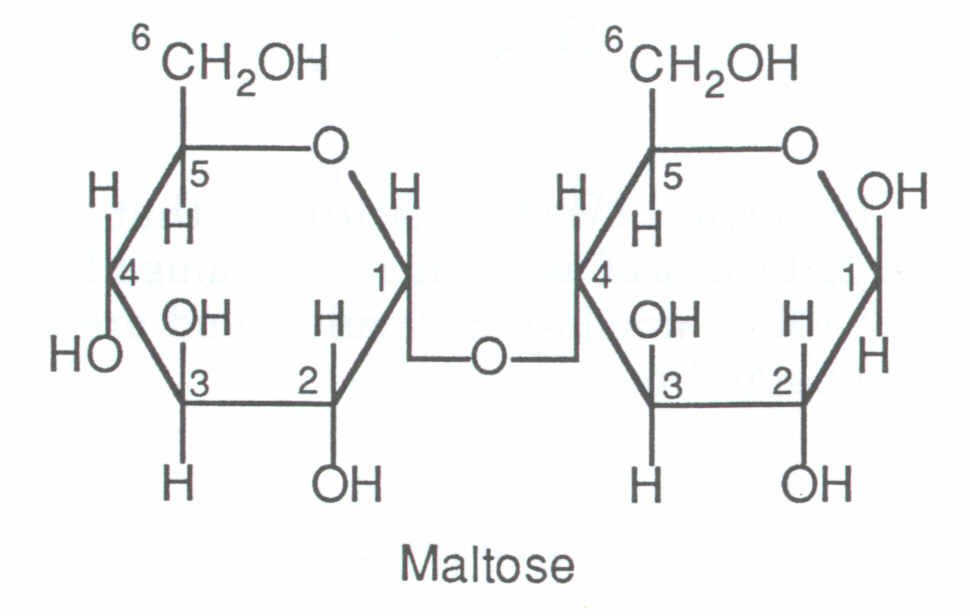
Image: theeducationinfo.com
The Glycosidic Linkage In Maltose Is Formed Between