Merchandise Inventory on the Balance Sheet: What Is It and Why Does It Matter?
Merchandise inventory refers to the physical goods a company holds for sale in the ordinary course of business. It represents the stock of goods that have been purchased or produced and are yet to be sold to customers. This includes raw materials, work-in-progress items, and finished goods ready for sale.
Classification on the Balance Sheet
On the financial statement known as the balance sheet, a company’s assets, liabilities, and equity are presented at a specific point in time. Merchandise inventory falls under the umbrella of current assets or short-term assets due to its liquidity. Current assets are defined as assets that are reasonably expected to be converted into cash or consumed within the upcoming fiscal year.
Within current assets, merchandise inventory is typically categorized as one of the following:
1. Raw Materials: These are the basic components or ingredients that go into making the finished product.
2. Work-in-Process Inventory: Goods that are still in the production process and have not yet been completed.
3. Finished Goods Inventory: Products that have been fully manufactured and are ready to be sold to customers.
Significance of Merchandise Inventory
Understanding the composition and amount of merchandise inventory on hand is vital for several critical reasons:
-
Cost of Goods Sold: Calculating the cost of goods sold (COGS) requires a precise count of merchandise inventory. COGS directly impacts a company’s profitability metrics, including gross profit and net income.
-
Profitability Analysis: By analyzing the inventory turnover ratios, businesses get valuable insights into how efficiently they manage their inventory. The rate at which inventory is being sold and replenished indicates the company’s ability to optimize cash flow and generate revenue.
-
Inventory Management: Monitoring inventory levels assists in balancing supply and demand while reducing the risk of stockouts and excessive storage costs. Having an optimal level of inventory without overstocking or being understocked helps improve profitability and customer satisfaction.
-
Planning and Forecasting: Inventory data supports effective planning for future production, sourcing, and sales activities. Accurate inventory records facilitate the prediction of upcoming supply and demand patterns.
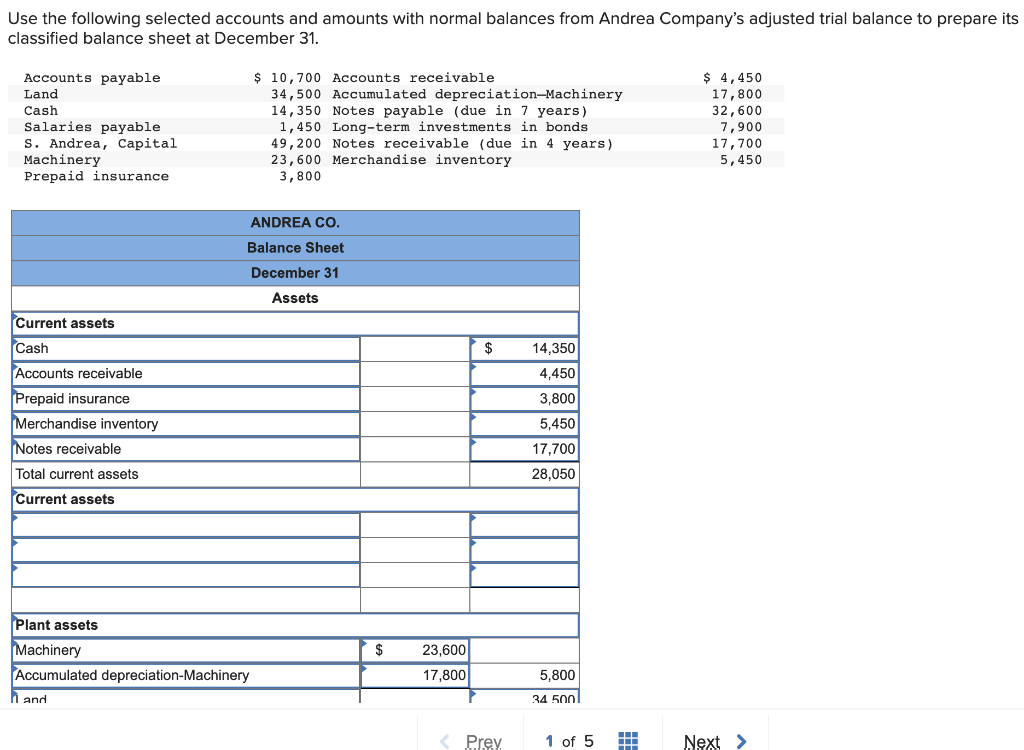
Image: www.chegg.com
Merchandise Inventory Is Classified On The Balance Sheet As A
Conclusion
Merchandise inventory is a strategic asset that plays a significant role in a business’s financial performance. Understanding its classification on the balance sheet and its impact on financial ratios provides a solid foundation for sound financial decision-making. Through effective merchandise inventory management, businesses can optimize cash flow, enhance profitability, and maintain a competitive edge in the market.
